The European Community chose, in 2008, to designate May 20 each year as a day to celebrate the importance of seas and oceans to the European people. By that action, the combined nations of Europe recognized that Europe is as much a maritime continent as a land continent.
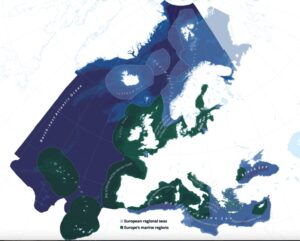
Consider these facts about the relationship of Europe to its coasts and marine environments. 23 of the EU’s 28 nations have a coastline. Europe has 70,000 km of coastline in all, bordering the Mediterranean, North, Baltic, Norwegian and Black Seas. That coastline is seven times as long at the U.S. coastline and 4 times as long as Russia’s. Almost half of Europe’s population lives in maritime regions, and 40% of the GDP comes from there. Europe’s maritime region is the largest of any nation in the world. In fact, Europe controls more marine territory than terrestrial territory!

However, that marine territory, although still highly productive, is not in good shape environmentally. About two-thirds of marine habitats and one-quarter of species conditions were deemed “unfavorable” by the EU in its latest report on ocean conditions. Invasive species are on the rise, with 320 new non-native species observed since 2000. Half of commercial fish stocks in European waters are fully or over-exploited, and fish catches have been declining over the past decade. Marine pollution continues to grow, with increasing worries about noise from shipping, renewable energy development and oil drilling. Plastic litter is also being recognized as an emerging issue, with most litter originating from land-based activities.
As a consequence, the EU has enacted an Integrated Marine Policy, or IMP, to govern uses and conservation of marine areas. The first objective of the IMP is “maximizing the sustainable use of the oceans and seas….” The objective includes efforts to reduce and adapt to climate change and reduce all forms of pollution. For fisheries, the objective includes eliminating discards of unwanted catches; outlawing harmful fishing practices; reducing illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing; and developing aquaculture that does not threaten wild fish stocks or create localized pollution.
The EU has also increased the pace of creating marine protected areas. Nearly 8000 protected sites exist, covering almost 6% of the total marine area. More than half of that area is in the Baltic and Mediterranean Seas.
European Maritime Day is one effort to raise the profile of marine conservation and to focus leaders annually on marine issues. Each year, a new theme is covered during a major conference held at rotating sites around Europe. The theme for the 2021 virtual meeting is “A green recovery for the blue economy.”
References:
European Commission. European Maritime Day. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/maritimeaffairs/maritimeday/en/about-emd. Accessed May 18, 2018.
European Commission. Maritime Affairs—Facts and figures. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/maritimeaffairs/documentation/facts_and_figures_en. Accessed May 18, 2018.
European Environment Agency. 2015. Europe’s seas: productive, but not healthy or clean. Available at: https://www.eea.europa.eu/media/newsreleases/europe2019s-seas-productive-but-not. Accessed May 18, 2018.
European Environment Agency. 2015. Marine protected areas in Europe’s seas. Available at: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/marine-protected-areas-in-europes. Accessed May 18, 2018.
European Parliament. The Integrated Maritime Policy. Available at: http://www.europarl.europa.eu/atyourservice/en/displayFtu.html?ftuId=FTU_3.3.8.html. Accessed May 18, 2018.
European Union. 2008. Joint Tripartite Declaration Establishing a “European Maritime Day.” Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/maritimeaffairs/maritimeday/sites/mare-emd/files/20080520_signed_declaration_en.pdf. Accessed May 18, 2018.
